At the heart of infrastructure and fluid transportation systems, every section of ductile iron pipeline carries not only water and gas, but also the pulse of urban development and the well-being of citizens. Here, quality is more than just empty talk; it’s a belief and commitment woven into every inch of steel and integrated into every process. DINSEN, fully aware of this crucial responsibility, embodies its unwavering pursuit of quality through absolute adherence to and exceeding the ISO2531 international standard, demonstrating a rigorous symphony of quality inspection for ISO2531 ductile iron pipes.
The standard specifies the technical requirements, test methods and quality control of ductile iron pipes, fittings, accessories and their interfaces used for water transportation (such as drinking water, irrigation water, etc.).
1. Ductile Iron Pipe DE
The outside diameter of the socket can be determined by measuring the circumference with a tape measure. Alternatively, two measurements with a caliper should be performed at perpendicular points across the cross section. The formula for ovality is: Ovality = (A1-A2)/(A1+A2).
2. Ductile Iron Pipe ID
The inner diameter of centrifugally cast ductile iron pipe is approximately equal to its nominal diameter, DN value, in millimeters.
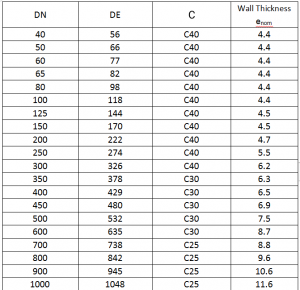
3. Ductile Iron Pipe Wall Thickness
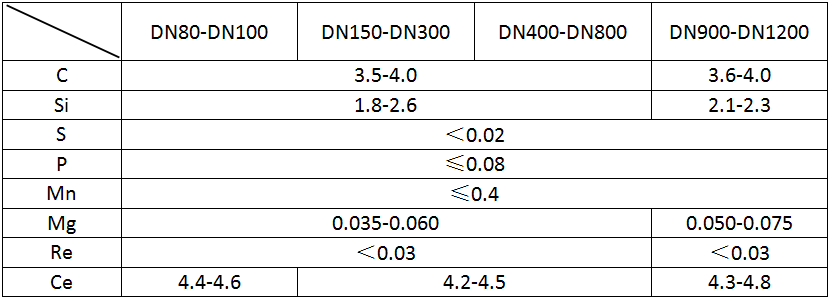
Use an ultrasonic thickness gauge with some coupling agent to stick to the location to be measured. The instrument accuracy is 0.1mm. The measurement position is at least two opposite locations on each end of the product. The measurement results are in accordance with the following table:
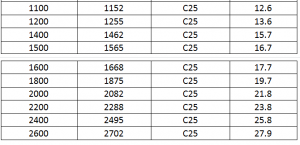
4. Ductile Iron Pipe Length
5. Ellipticity
The out-of-roundness of the cast pipe cross section.
Ovality = 100 x (A1-A2) / (A1+A2)
A1: max A2: Mini
6. Straightness
Cast pipes should be straight, with a maximum deviation not exceeding 0.125% of the effective length (6000 x 0.125% = 7.5mm). If the pipe is unobstructed, visual inspection should be used for straightness. In case of doubt, the following method should be used. Roll the pipe axially on two stands or rollers to check its straightness. The spacing between the stands/rollers should be at least 2/3 of the standard length of the pipe. The point of maximum deviation from straightness should be determined, and the deviation should not exceed the limit of 7.5mm.
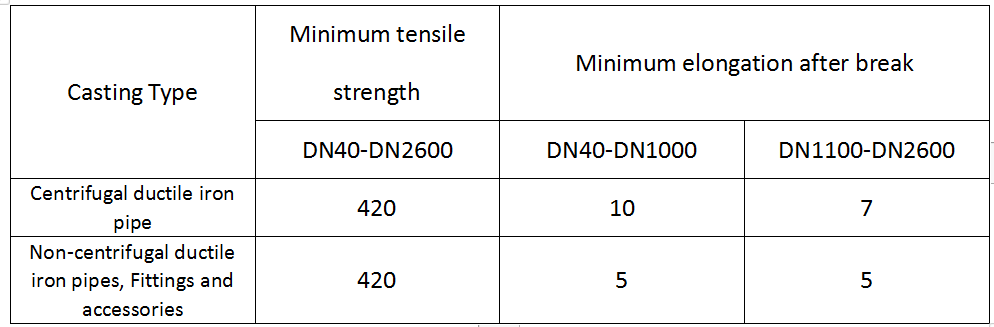
7. Tensile properties
The eligibility criteria are as follows:
Failure criteria: Take two test bars from the same sample ring for testing. If the mechanical properties of one test bar in the duplicate sample fail to meet the requirements, the batch of pipes will be reviewed and the failure handling process will be implemented.
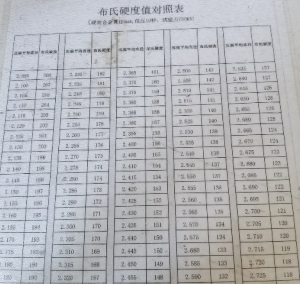
8. Brinell hardness
The Brinell hardness tester operates by pressing a steel ball of a specified diameter into the specimen surface at a specified speed under a specified test force. The force is then removed after the specified test force is maintained for a specified time. The Brinell hardness of the metal is expressed as the average pressure applied over the spherical surface area of the indentation. The Brinell hardness test is unaffected by microscopic segregation or compositional inhomogeneities in the specimen. By calculating the ratio of indentation area to applied load, it objectively assesses material properties such as ductility and wear resistance, and is often used as a reference standard for industrial quality control.
The Brinell hardness of centrifugal ductile iron pipes shall not exceed 230 HBW, and the Brinell hardness of non-centrifugal ductile iron pipes, fittings and accessories shall not exceed 250 HBW. The heat affected zone of welded parts is allowed to have a higher Brinell hardness value.
9. Chemical composition of ductile iron, spectral detection
Spectroscopic methods can analyze the content of key elements such as silicon and magnesium in ductile iron in real time (for example, the final silicon content directly affects the low-temperature impact toughness of ferritic ductile iron), replacing traditional chemical methods for high-speed testing and guiding pre-cast process adjustments. By measuring the distribution of elements such as carbon and sulfur, we ensure that the graphite nodularity rate (spheroidization rate ≥90%) meets the required tensile strength (≥420 MPa) and elongation (≥10%). Real-time monitoring of metal composition during the casting process reduces scrap and improves the internal quality of ductile iron pipes and fittings.
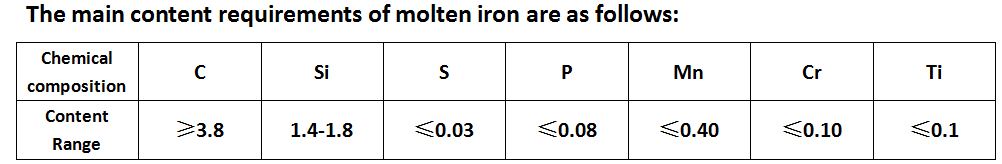
Control requirements for main components of molten iron after spheroidization
Get the full quality inspection report
Post time: Sep-11-2025