DINSEN Metal is committed to the field of metal processing and stainless steel products. It is proficient in various metal processing processes and has achieved remarkable results in the research and development and production of stainless steel fixing products, clamps, joints, coupling, pipes and fittings etc. It brings high-quality and diversified metal products to the market and has established a good reputation in the industry with its high-quality product quality and exquisite craftsmanship.
Metal processing, taking clamp products as an example
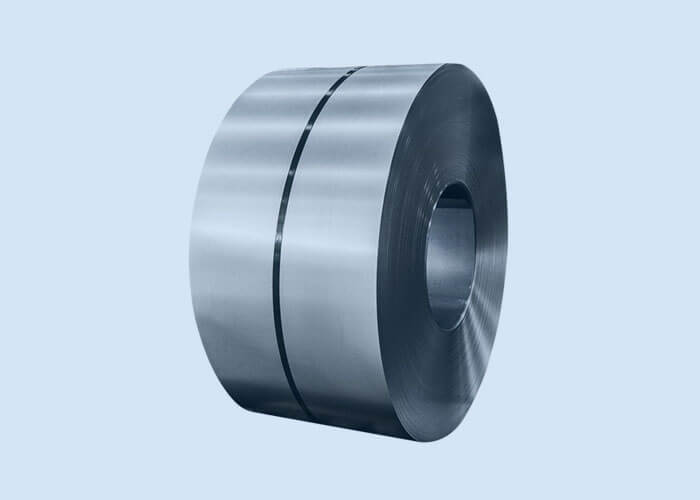
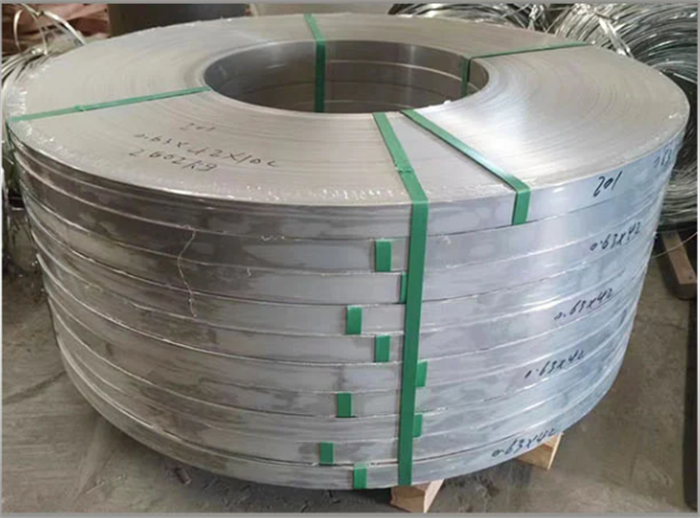
1.Raw Material
Raw material selection: Common materials are stainless steel (such as 304, 316), carbon steel (Q235) or galvanized steel strip, which can be selected according to corrosion resistance, strength and cost requirements.
Steel strip slitting: The large steel strip is cut into the required width (such as 10mm, 12mm) by a slitting machine to ensure dimensional accuracy and edge flatness.
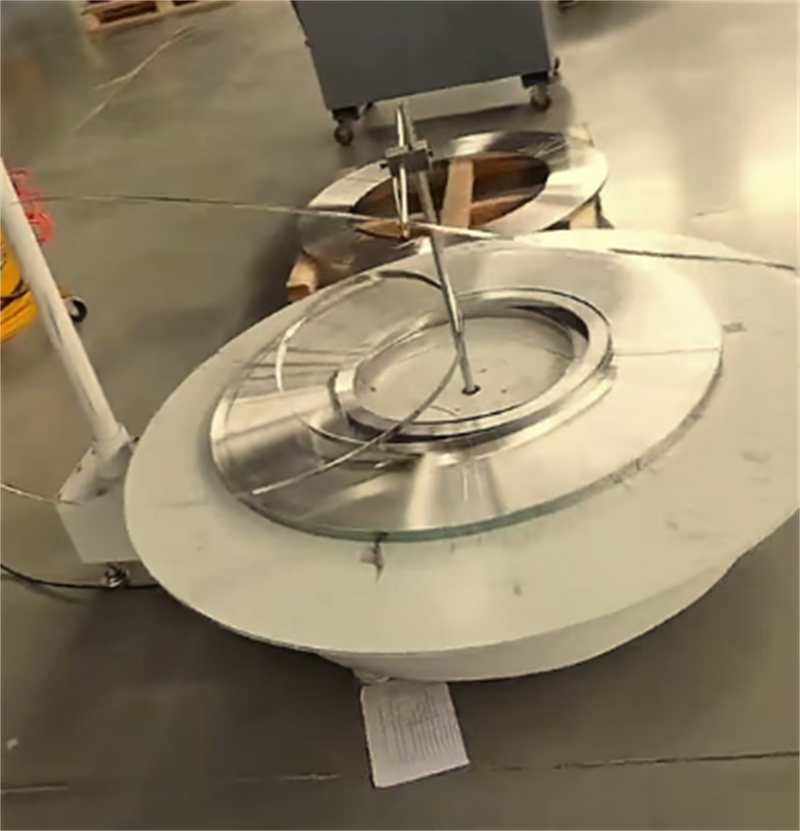
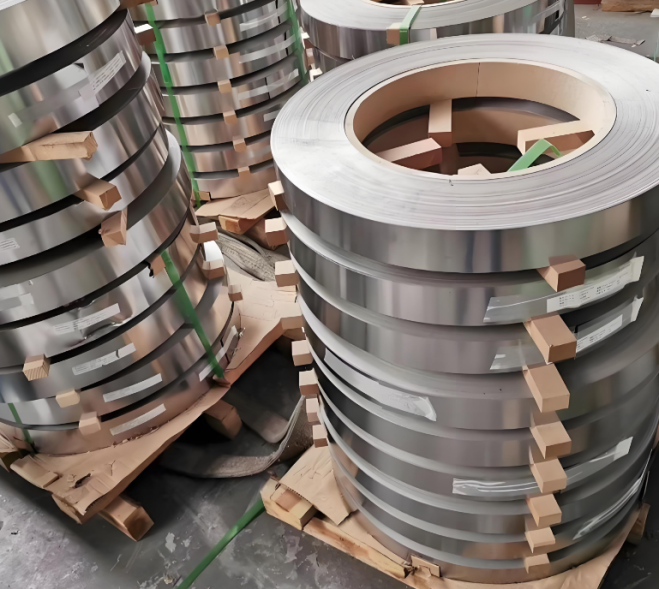




2. Stamping
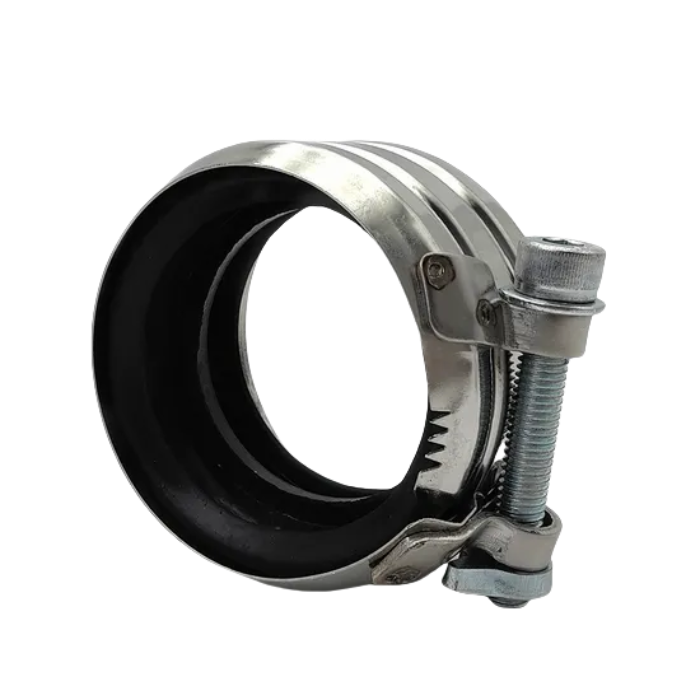
Stamping die design: Design the die according to the type of throat clamp (such as worm type, bolt type) to punch out the throat clamp body (steel belt), locking ear, threaded hole and other structures.
Steel belt stamping: Use a punch press and a continuous die to stamp the steel belt into a ring belt with tooth patterns (to enhance friction) and process the locking mechanism (such as worm gear grooves or bolt holes).
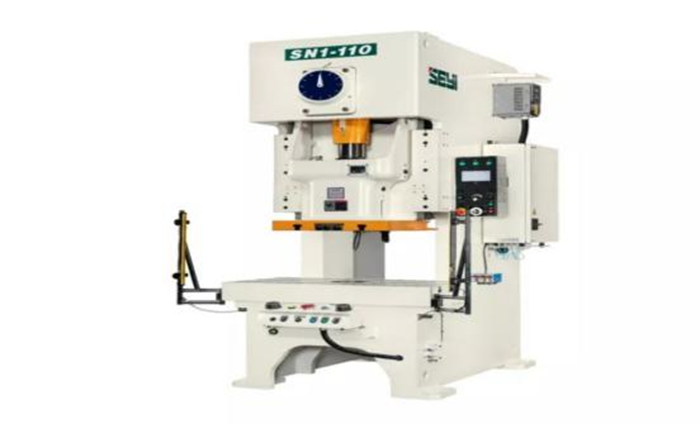
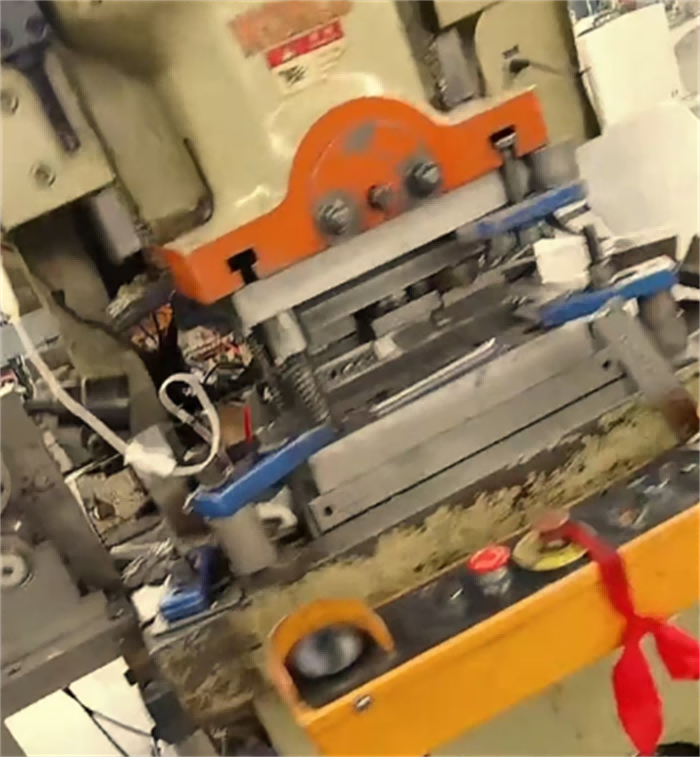

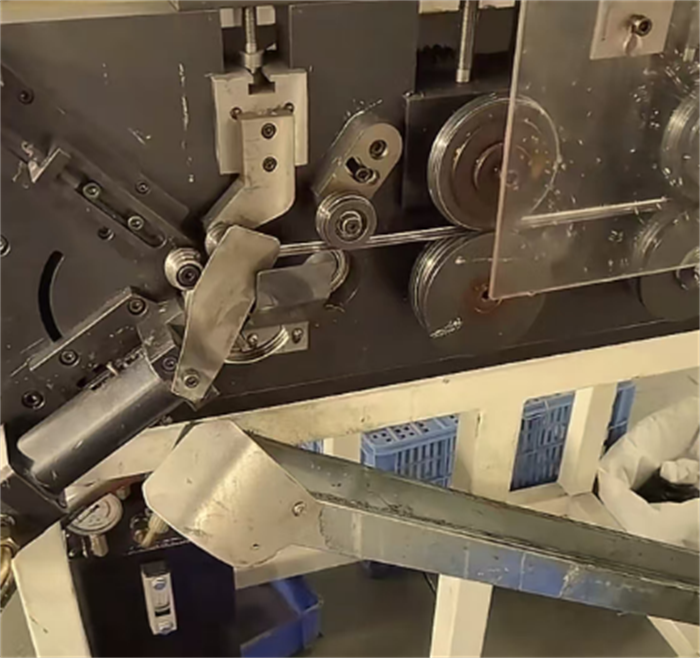
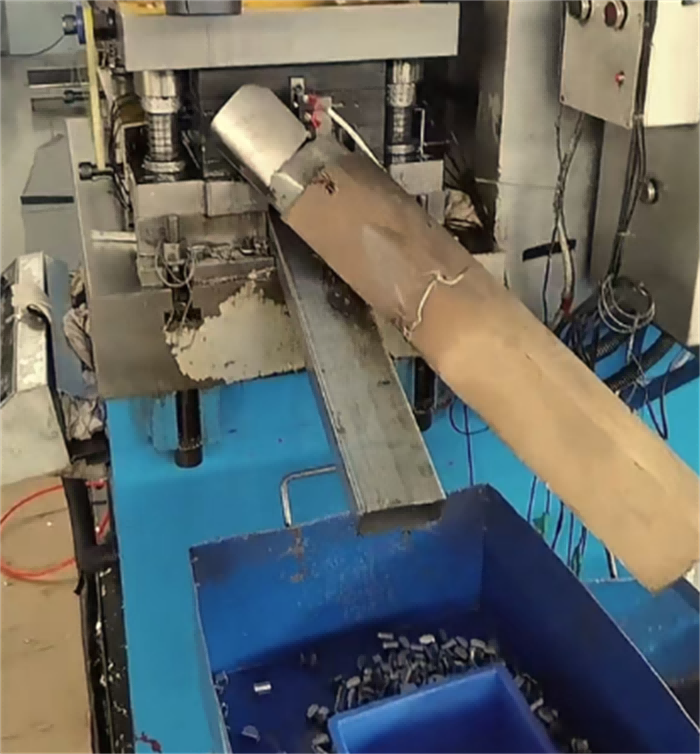

3.Welding
Spot welding/laser welding: The locking mechanism (such as worm seat, bolt base) is welded and fixed to the steel strip to ensure the strength and burr-free of the weld.
Automated welding: High-precision throat clamps are welded by robot laser to improve efficiency and consistency.
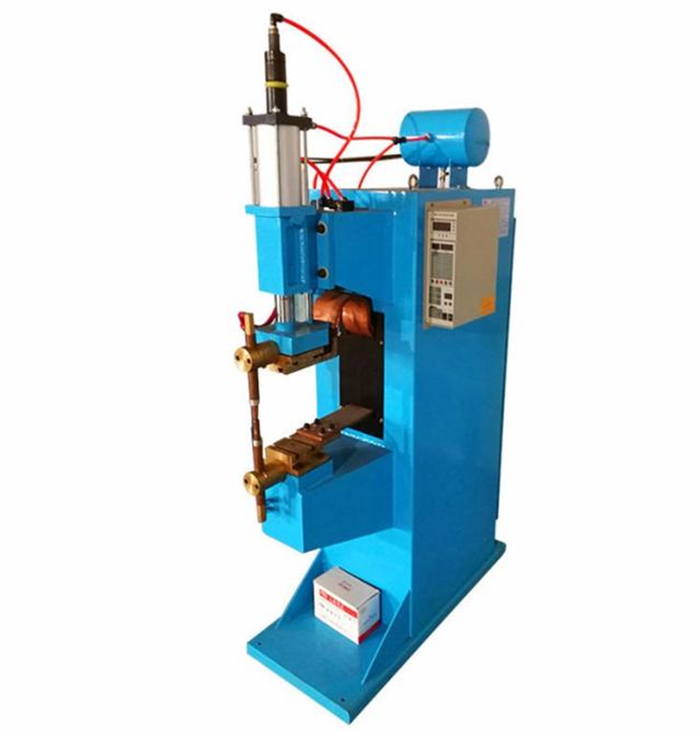
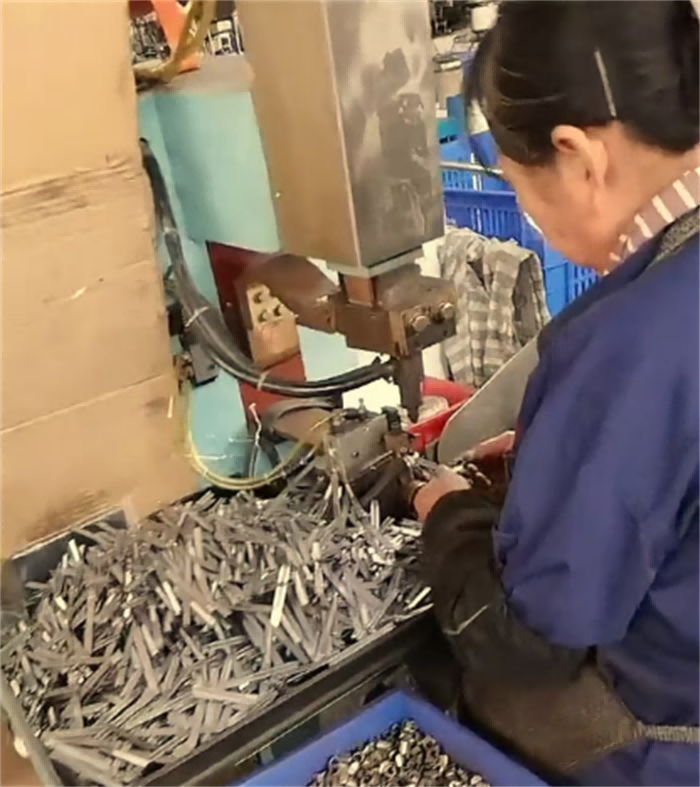
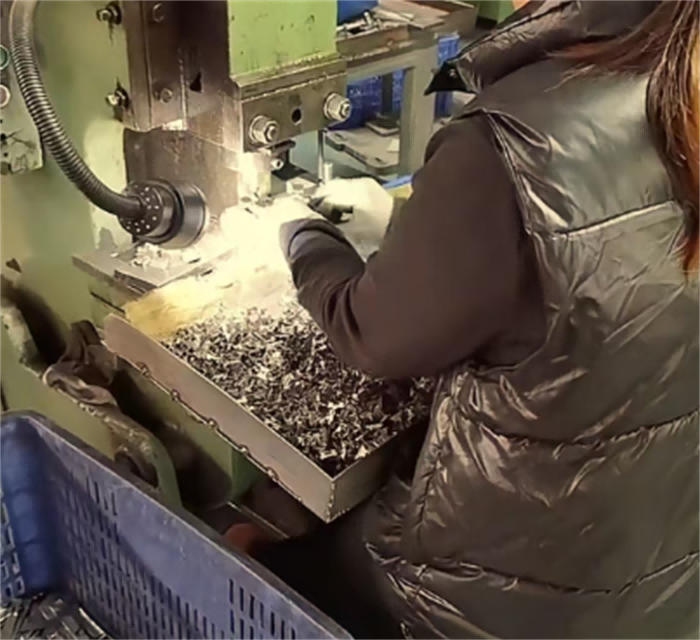


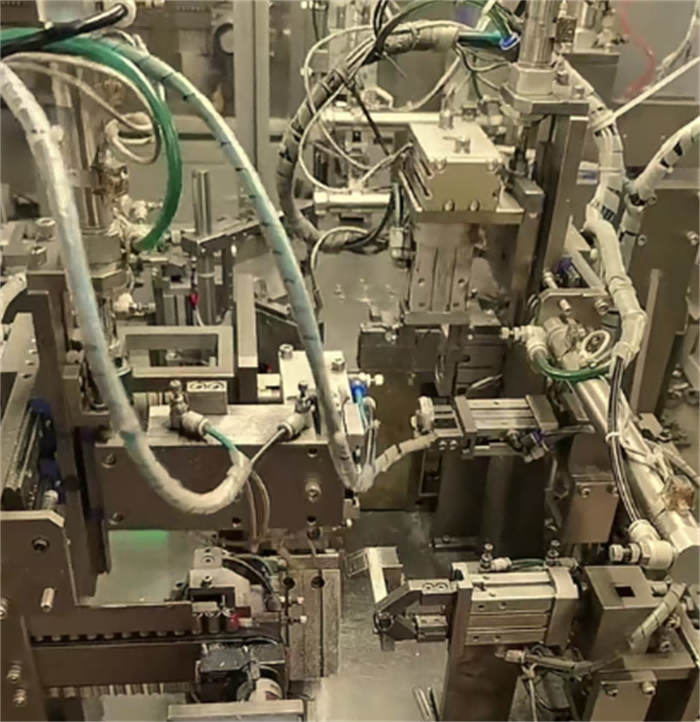

4. Surface Treatment
Electroplating/spraying: Carbon steel materials need to be treated to prevent rust, such as zinc plating (white zinc, colored zinc), nickel plating or epoxy resin spraying.
Passivation treatment: Stainless steel hose clamps are passivated by pickling to enhance corrosion resistance.
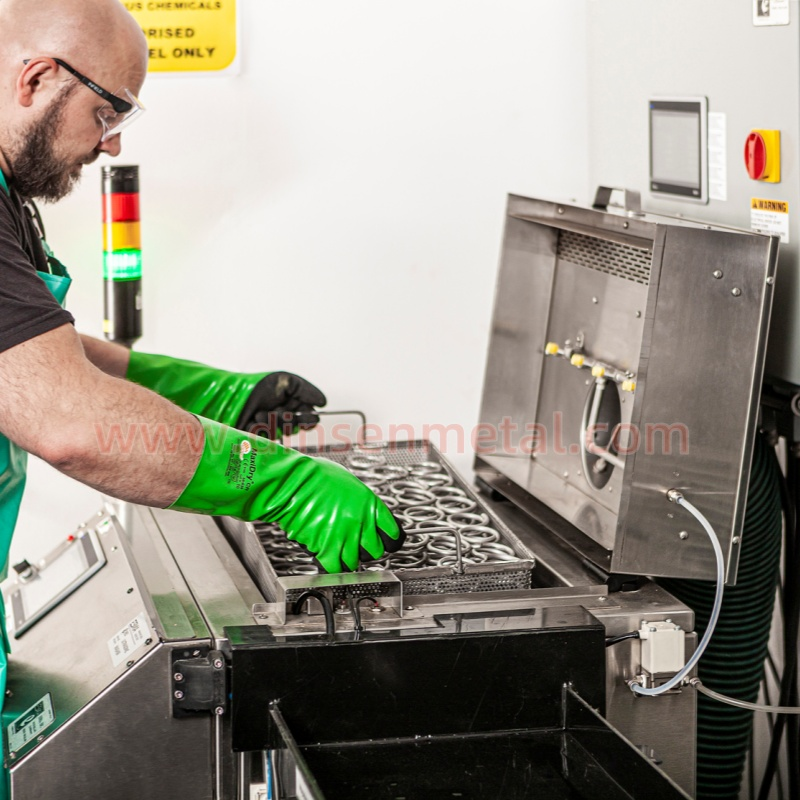


Passivation treatment
5.Assembly and Locking
Worm-type throat clamp: install the worm gear assembly, fix the worm seat by riveting or welding to ensure smooth rotation.
Bolt-type throat clamp: drill and tap holes at both ends of the steel belt, install bolts and nuts, and calibrate the thread matching accuracy.

6. Quality Inspection
Dimension detection: Use calipers and projectors to measure the inner diameter of the throat clamp, the thickness of the steel belt, and the position of the locking mechanism.
Strength test: Use a tensile testing machine to test the clamping force of the throat clamp (such as tensile strength≥500MPa) and the durability of the locking mechanism.
Corrosion resistance test: Salt spray test (such as 48-96 hours) to verify the coating or passivation effect
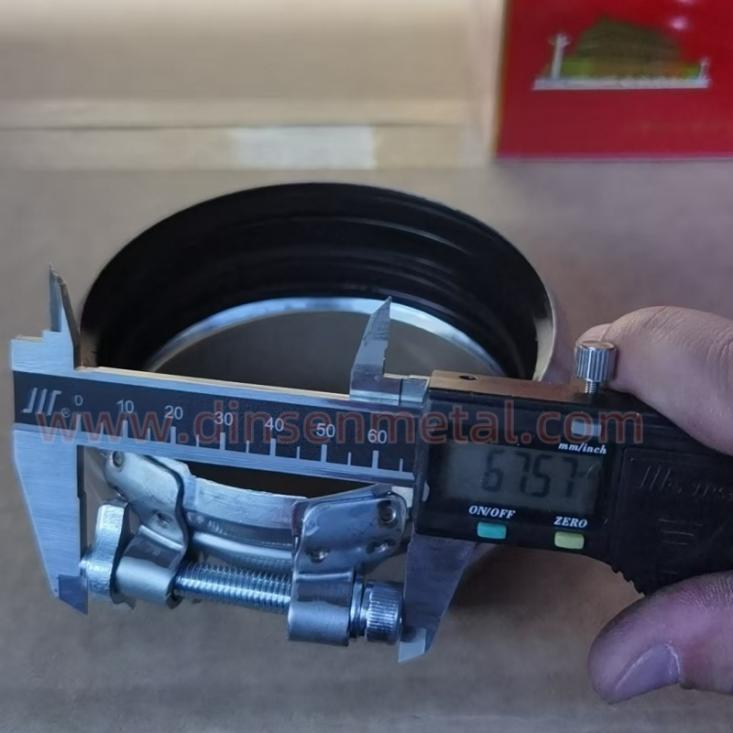
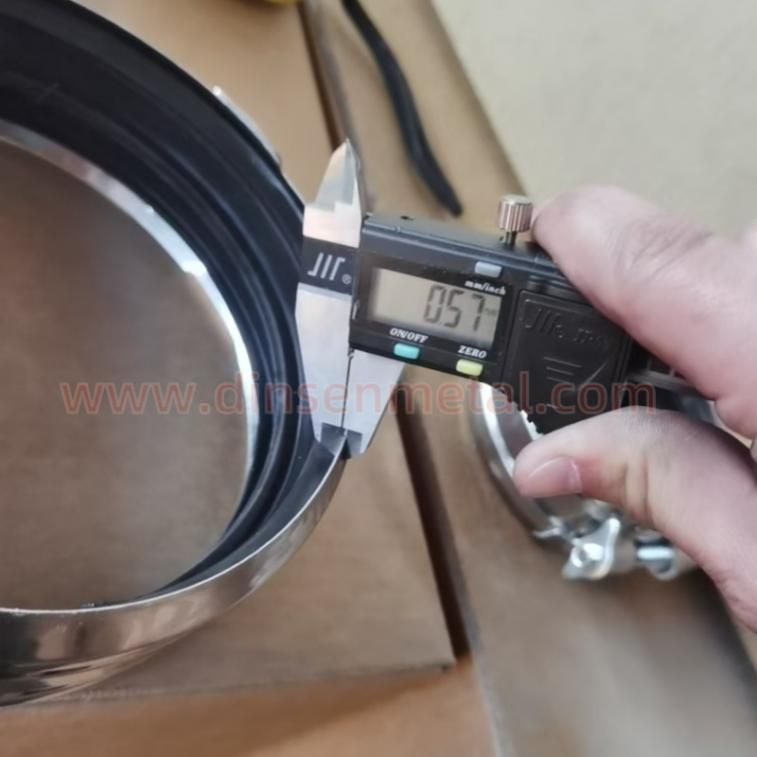
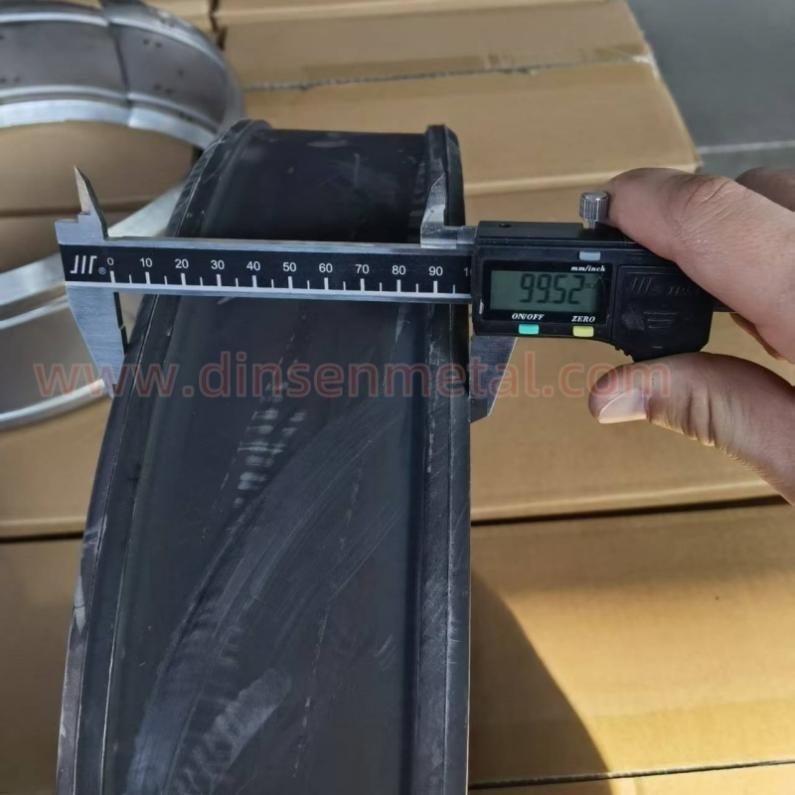
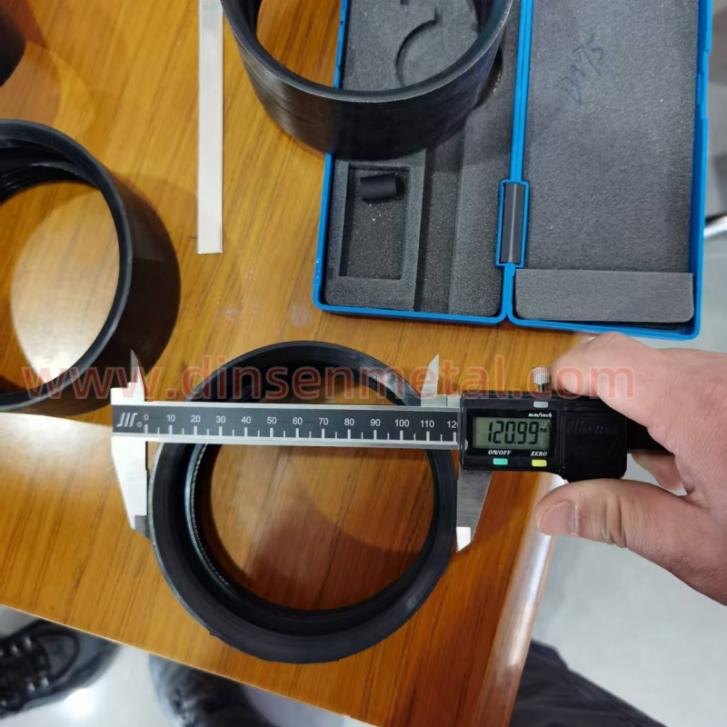





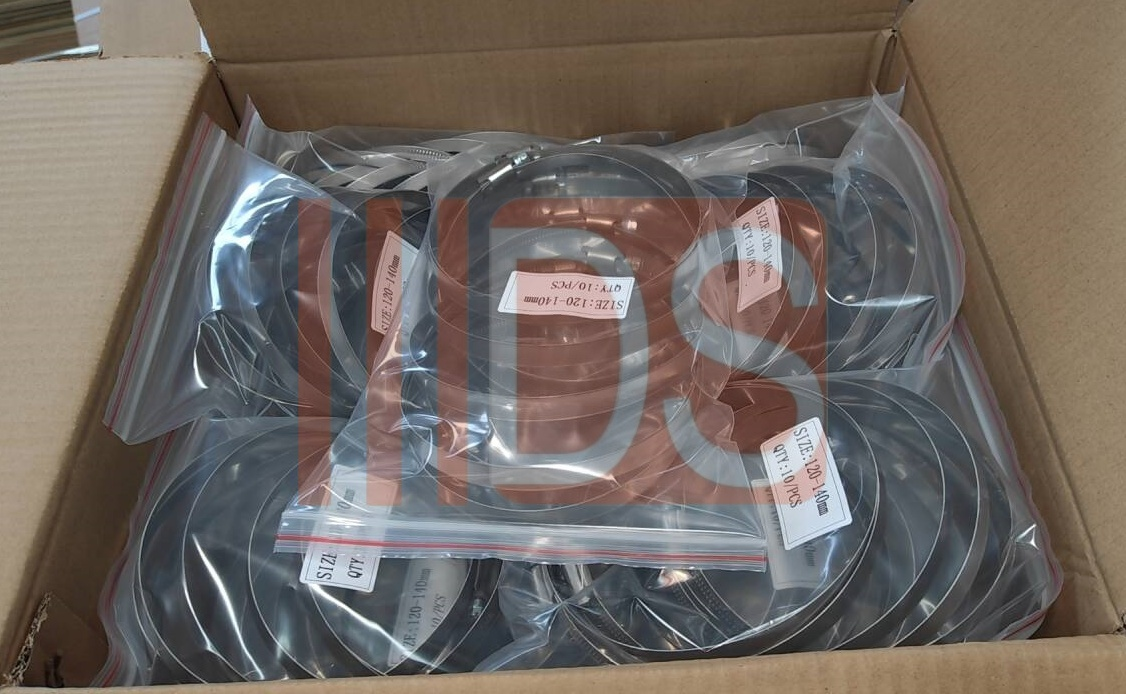
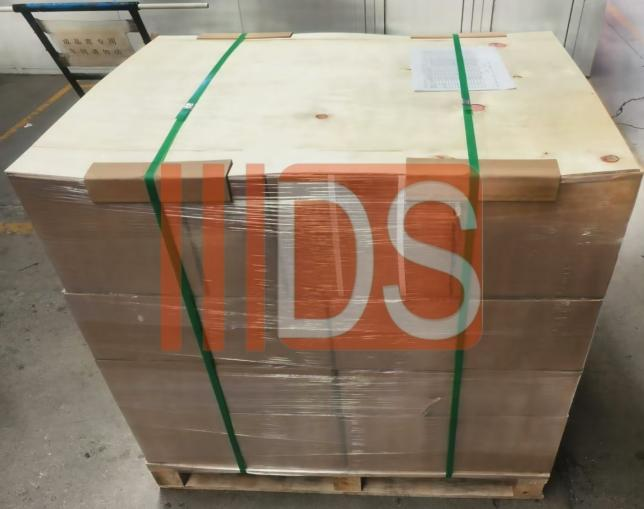
7.Packing
Carton packaging or plastic sealed bag packaging to prevent rust during transportation and storage.
Classification and identification: Pack by specification and material, and mark the model, batch and production date.











